p-n Junction Diode - Forward and Reverse Bias Characteristics
p-n Junction Diode - Forward and Reverse Bias Characteristics: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Forward Biasing of Junction Diode, Reverse Biasing of Junction Diode, Zener Breakdown & Expression for Variation of Current with Voltage of P-N Junction Diode etc.
Important Questions on p-n Junction Diode - Forward and Reverse Bias Characteristics
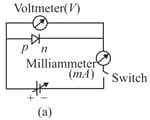
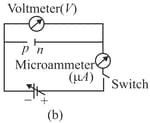
Which of the following circuit diagram of p – n junction diode is (i) forward bias and in (ii) reverse bias:
The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped P-N junction under reverse biased condition is called _____ breakdown.
Low doping required for Avalanche breakdown in diodes.
The breakdown that occurs in reverse bias conditions in a narrow junction diode is known as
Pick out the incorrect statement regarding reverse saturation current in the p-n junction diode.
The reverse saturation current in a p-n junction diode is due to only the;
Is reverse saturation current dependent upon the change in temperature ? Explain.
What is reverse saturation current in diode ? Why it is temperature dependent ?
Reverse bias applied to a junction diode.
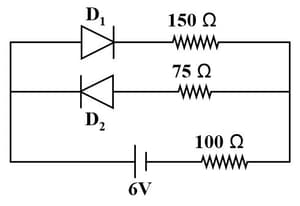
Currents flowing in each of the following circuits and respectively are
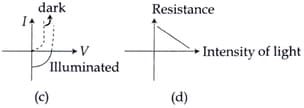
Identify the semiconductor devices whose characteristics are given below, in the order :
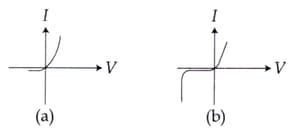
The forward-biased diode connection among the following is:
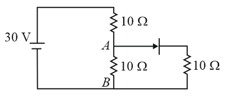
Find for the circuit given below.
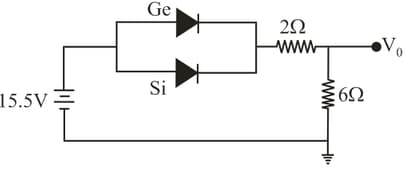
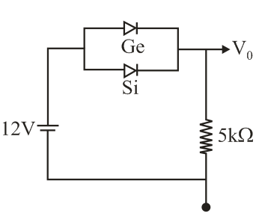
Ge & Si diodes conduct at knee voltage & respectively. If Ge diode connection are reversed, then value of changes by , what is the value of ?
In the circuit shown in figure, find the magnitude of maximum potential difference (in ) between
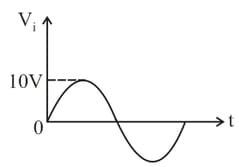
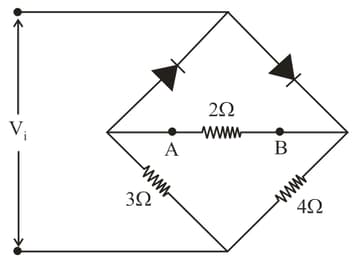
Calculate the value of output voltage (in )(to the closest integer) if the Si diode and Ge diode conduct at and respectively as shown in figure.
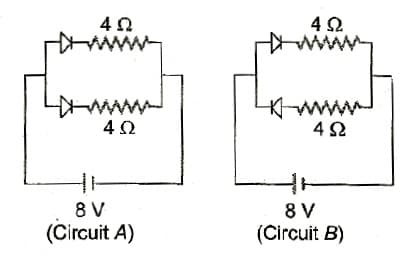
Two identical PN junction are joined in series with a battery shown below. For which potential drop is same.
The circuit contains two diodes each with a forward resistance of and with infinite reverse resistance. If the battery voltage is the current through the resistance is
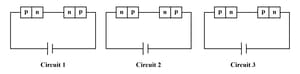
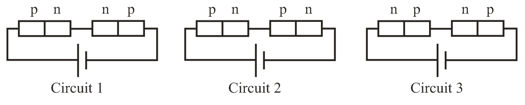
Two identical junctions may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two junctions are equal in
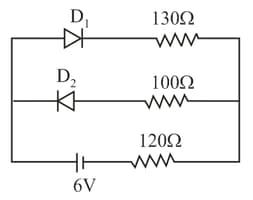
The circuit shown below contains two ideal diodes, each with a forward resistance of If the battery voltage is the current through the resistance (in amperes) is: